National Vocational Qualification Levels
The Tertiary and Vocational Education Commission (TVEC) has taken necessary steps to introduce the National Vocational Qualification (NVQ) System with 7 Levels. The NVQ level 7 is equivalent to the bachelor degree qualification. Students can enroll into the M.Sc. or any other postgraduate programme after completion the NVQ level 7. Students who have successfully completed NVQ level 5, can enter for the 2nd year in most of the foreign universities where the relevant field is available.
Compared to the academic qualifications, the NVQ is designed for the job seekers soon after their A/L exams. The speciality of the NVQ system is that, at the completion of each level of the NVQ qualification, candidates become eligible to enter the professional job market with fairly higher salary scales than the academic qualification holders.
Many developed and developing countries in the world have introduced vocational skills certification systems similar to the NVQ system. As such, the NVQ system is in real practice and quite familiar to the authorities in most of the countries. Therefore, the National Vocational Qualification System is nationally and internationally recognized in order to enter the global job market as qualified professionals.
NVQ Levels in Sri Lanka
Sri Lankan Qualifications Framework
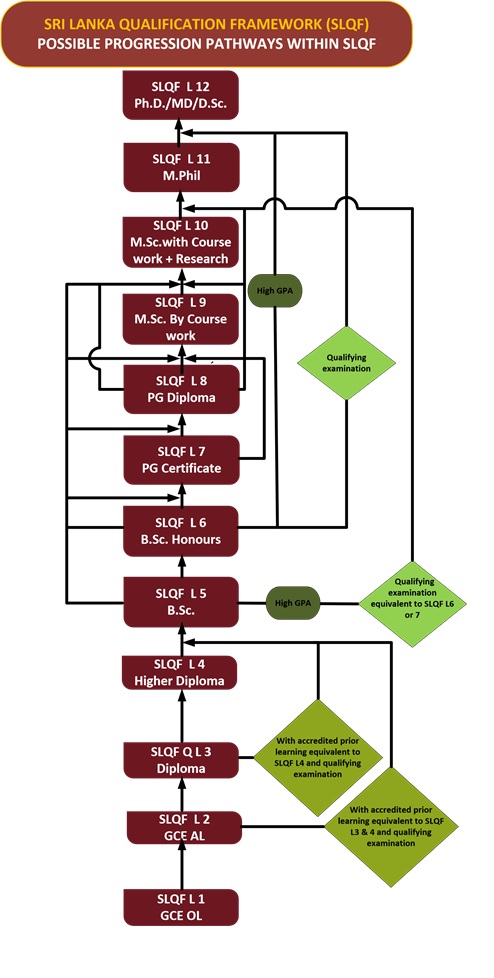
The SLQF is a nationally consistent framework for all higher education qualifications offered in Sri Lanka. The SLQF applies to all higher education institutions both public and private, which provide post-secondary education. It recognizes the volume of learning of students and identifies the learning outcomes that are to be achieved by the qualification holders. The SLQF comprises twelve levels and the descriptors of each of these levels are comprehensively defined. Since the volume of learning is considered in the SLQF, the number of credits that should be earned by students for each qualification is also given. With the objective of having a uniform system in naming a qualification, the designators and qualifiers of each qualification have been identified in the SLQF. The abbreviations for each qualification were also identified to maintain uniformity. The purposes and scope, and attributes expected for the award of each qualification, as well as the minimum admission requirements along with possible progression opportunities are also stated in the SLQF.
The SLQF integrates the National Vocational Qualifications Framework (NVQF) developed by the Tertiary and Vocational Education Commission and the pathways of lateral mobility between the vocational education sector and the higher education sector have also been identified. The SLQF helps in the recognition of accredited prior learning in order to facilitate the vertical mobility within the higher education system.
With the globalization of higher education, national qualifications frameworks have been developed in many countries. These have not only helped to evaluate the higher educational qualifications obtained from different countries but also have facilitated the appropriate international interpretation of national qualification levels. The SLQF also contributes to the evaluation of qualifications obtained from cross border higher education institutions as the levels identified in this framework are based on the learning outcomes of the qualification holders. The SLQF will assist in the evaluation and recognition of qualifications offered by Sri Lankan higher education institutions and this will be useful to the qualification holders to identify the level of their qualifications. In addition, the SLQF will assist potential employers to know the level of learning and the attributes of a particular qualification holder.
The SLQF is useful to the higher education institutions, both in the state sector and non-state sector in designing courses as the minimum level of learning outcomes required for each qualification is indicated by the minimum number of credits that should be earned by a qualification holder. Thus, the SLQF will contribute towards strengthening the quality of higher education qualifications offered by universities and other higher education institutions in Sri Lanka.
The SLQF does not deal with the designing and offering of short term courses by any higher education institution that will meet specific learning outcomes. These courses may be of a few months duration and a certificate may be awarded on completion of such courses. Those certificates are not aligned with the qualifications identified in the SLQF. In addition, honorary degrees and certificates of attendance are not included in the SLQF. The honorary doctorate is differentiated from doctoral degrees in the SLQF
NVQ Levels and SLQF
Sri Lankan Qualification Framework (SLQF) &
National Vocational Qualification (NVQ)
Comparable Levels
Sri Lankan Qualification Framework (SLQF)
Possible Progression Pathways NVQ 7 to SLQF
For more Details about SLQF Click here to download








No comments:
Post a Comment